The field of personal development has gained significant traction over the past few decades, emerging as a pivotal area of interest for both individuals seeking self-improvement and scholars examining the underlying principles that inform this pursuit.
“Theoretical Foundations of Personal Development: An Academic Perspective” endeavors to explore the multifaceted theories that contribute to the understanding of personal growth and transformation.
Drawing upon a diverse array of disciplines, including psychology, sociology, and educational theory, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the conceptual frameworks that underpin personal development practices.
By elucidating key theories such as Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, Bandura’s social learning theory, and the constructivist approaches to learning, the article seeks to bridge the gap between empirical research and practical applications.
Additionally, it will highlight the significance of individual agency, motivation, and the sociocultural context in shaping personal development trajectories. Through a rigorous academic lens, this exploration not only affirms the relevance of theoretical insights in guiding personal development strategies but also encourages a deeper appreciation for the complexities inherent in human growth.
Ultimately, this article aspires to contribute to the ongoing dialogue surrounding personal development by providing a solid theoretical foundation that informs practice and policy.
- Overview of Personal Development Theories
Personal development theories encompass a range of frameworks that seek to explain the processes through which individuals grow, change, and realize their potential. These theories often draw from various disciplines, including psychology, sociology, and education, to provide insights into the factors influencing personal growth.
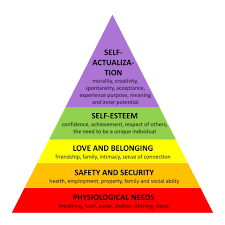
Prominent theories such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development illustrate the complexity of human motivation and the necessity for individuals to navigate various life stages.
Furthermore, socio-cognitive theories emphasize the role of observational learning and self-efficacy in shaping personal development, showcasing how individuals can adapt and thrive within their environments.
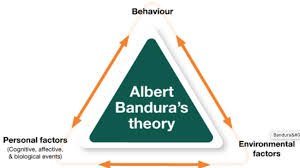
Additionally, the interplay between internal and external factors is crucial in understanding personal development. Theories such as Bandura’s social learning theory highlight the importance of social context and modeling in personal growth.
Similarly, humanistic approaches, like those proposed by Carl Rogers, underscore the significance of self-actualization and the need for an environment conducive to growth.
Collectively, these diverse theoretical perspectives contribute to a richer understanding of the multifaceted nature of personal development, revealing how individual experiences and broader societal influences intertwine to shape one’s journey toward self-improvement and fulfillment.
Studies employing longitudinal designs have reported significant improvements in self-esteem, emotional regulation, and overall life satisfaction among participants engaged in structured personal development programs.
- Historical Context of Developmental Frameworks
The evolution of developmental frameworks is deeply rooted in historical contexts that reflect shifts in societal values, scientific understanding, and cultural narratives. During the early 20th century, significant advancements in psychology, notably through the works of psychologists like Sigmund Freud and Jean Piaget, laid the groundwork for understanding human behavior and cognitive development.
Freud’s psychoanalytic theory introduced a focus on the unconscious mind and childhood experiences, while Piaget’s research emphasized the stages of cognitive development in children, highlighting the importance of active engagement with the environment. These foundational theories emerged against a backdrop of rapid industrialization and changing social structures, prompting a reevaluation of education and developmental processes.
As the mid-20th century approached, the dialogue surrounding personal development expanded to incorporate broader socio-cultural elements. The rise of humanistic psychology, championed by figures such as Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow, shifted attention towards self-actualization and the intrinsic potential of individuals.
This period also saw an increased emphasis on the role of culture and environment in shaping personal development, with theorists like Lev Vygotsky advocating for a sociocultural perspective.
Ultimately, the historical trajectory of developmental frameworks reveals an ongoing effort to integrate diverse influences—from psychological theories to cultural contexts—into a cohesive understanding of how individuals evolve throughout their lives.
- Key Theorists Influencing Personal Growth
The contributions of key theorists such as Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers significantly shaped the landscape of personal growth through their emphasis on humanistic psychology. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs framework posits that individuals are motivated by a series of needs, culminating in self-actualization, which reflects the full realization of one’s potential.
This perspective underscores the belief that personal growth is a dynamic process influenced by the fulfillment of fundamental human needs, thereby encouraging individuals to pursue their highest aspirations.
Concurrently, Carl Rogers’ client-centered therapy introduced the notion of unconditional positive regard, emphasizing the importance of an empathetic and accepting environment in fostering self-discovery and personal development. Rogers’ focus on the subjective experience of individuals underscores the importance of self-awareness and authenticity in the journey toward personal growth.
In addition, the work of Albert Bandura introduced the concept of self-efficacy, which underscores the role of belief in one’s abilities in achieving personal goals. Bandura’s social cognitive theory highlights the interplay between individual agency, environmental factors, and observational learning, suggesting that personal growth can be significantly influenced by social contexts and role models.
Together, these theorists have contributed to a more holistic understanding of personal development, integrating psychological insights with an appreciation for the complex interplay of individual agency, social influence, and the pursuit of potential, thereby enriching contemporary approaches to personal growth.
Check out more on Personal Development
- Empirical Evidence Supporting Personal Development
Extensive empirical research has substantiated the principles underlying personal development, demonstrating a robust correlation between targeted personal growth interventions and enhanced psychological well-being.
Studies employing longitudinal designs have reported significant improvements in self-esteem, emotional regulation, and overall life satisfaction among participants engaged in structured personal development programs.
For instance, randomized controlled trials have illustrated that individuals who undergo coaching or participate in workshops designed to develop specific skills exhibit not only improved performance in their professional domains but also greater resilience in facing life’s challenges. These findings reinforce the validity of personal development as a transformative process, suggesting that structured interventions can lead to measurable positive changes in individuals’ lives.
Moreover, meta-analyses of various personal development methodologies, such as mindfulness training and cognitive-behavioral approaches, have revealed consistent benefits in enhancing psychological flexibility and decreasing anxiety levels.
The systematic examination of these interventions indicates that the principles of personal growth are not merely anecdotal but are supported by rigorous evidence that highlights their efficacy. Such empirical documentation not only strengthens the case for personal development practices but also provides a foundation for further exploration into innovative strategies that foster individual growth and well-being.
- Future Directions in Developmental Research
Future developmental research is likely to explore the intersection of technology and personal growth methodologies, particularly as digital platforms gain prominence in delivering interventions. The rise of mobile applications and online coaching presents opportunities for personalized and scalable approaches to personal development, warranting rigorous investigation into their efficacy and user engagement.
Additionally, understanding the nuances of how cultural contexts influence personal development experiences is poised to be a critical area of inquiry. By examining diverse populations and their unique developmental pathways, researchers can enhance the applicability and inclusivity of personal development frameworks.
Furthermore, longitudinal studies that track individuals over extended periods are essential for discerning the long-term effects of personal development practices. Such research could provide insights into the sustainability of positive changes and the potential for relapse in unhealthy behaviors.
Emphasis on interdisciplinary approaches that integrate psychology, sociology, and education will enrich the understanding of personal development as a multifaceted phenomenon.
Exploring the role of social support networks and peer influences in personal growth processes could also yield valuable findings, ultimately contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of how individuals navigate their personal development journeys.
In conclusion, the exploration of the theoretical foundations of personal development reveals a rich tapestry of psychological, sociocultural, and philosophical frameworks that inform the practice and understanding of individual growth.
The integration of theories such as Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, Bandura’s social learning theory, and the principles of constructivist learning underscores the complexity of personal development as a multifaceted discipline. This academic perspective not only highlights the diverse influences on personal growth but also emphasizes the importance of contextual factors in shaping individual experiences.
Future research in this domain holds the potential to further elucidate the interplay between theory and practice, ultimately enhancing the efficacy of personal development initiatives across various settings.